Eating during pregnancy, the microbiological risks

Eating safe food is important for everyone’s health, but it is even more so for some categories of people that are more sensitive. Pregnant women represent one of these categories. In fact, after the conception, women’s body starts to change and this can make them more vulnerable and exposed to the possibility of contracting a foodborne disease. In these cases, it is not only the health of the mother that is at risk, but also the one of the child. Some of these diseases can have serious consequences for the foetus and could compromise its normal development.
Microbiological risks
For both the mother and the foetus the most probable risks related to food are biological risks. These risks are due to bacteria, parasites and viruses that can contaminate foods. The most dangerous pathogens for the foetus are in particular Toxoplasma, Listeria, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Escherichia coli, Hepatitis A virus and Norovirus.
In most cases, the most serious consequences deriving from the presence of these pathogens are premature birth, foetal death and abortion. Some pathogens, instead, are characterized by the appearance of specific consequences: this is the case of Toxoplasma, which can cause malformations or serious brain lesions of the foetus.
What to do to reduce these risks?
Pregnant women can reduce the biological risks of food by adopting a few simple precautions. In fact, they have to:
- avoid the consumption of raw or undercooked foods, some types in particular like fruit and vegetables, meat and sausages, fish and seafood, soft and fresh cheeses derived from raw milk;
- pay attention to the methods of preparation, storage and consumption of food, adopting good hygiene and health practices.
The “Foods & Pregnancy” project
To assess the actual knowledge of pregnant women in Italy about food risks, and promote correct practices of food handling among them, in 2017 the Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale delle Venezie (IZSVe, an Italian health authority in the fields of animal health and food safety) conducted a research and communication project about this issue.
The project was funded by the Italian Ministry of Health and has been articulated in three steps, the first two serving as target audience analysis. First, the knowledge of the Italian women was investigated through both a national survey and web monitoring activities that focused on Facebook groups dedicated to the pregnancy topic. In fact, social media are a common way to spread fake news and wrong beliefs among pregnant women.
Second, a series of meetings (World Cafè) between food safety experts, nutritionists, gynecologists and pregnant women were organized in the Veneto area (where the IZSVe headquarters are placed). This participatory process enabled fruitful discussions between experts and non-experts and facilitated a deeper understanding of pregnant women’s behaviours, beliefs and information needs. At the same time, pregnant women were given scientifically sound information about food risks during pregnancy as a countermeasure to recognise and debunk the fake news they could encounter.
The communication campaign
Basing on the insights collected during the meetings and the web monitoring activities, a flyer with a summary of the main information about biological risks during pregnancy and the way to reduce the risks was designed in different languages (Italian, English, French, Romanian, Arabic, Chinese, Russian). The flyer was distributed to hospital obstetric wards and gynaecological clinics and doctor’s offices in the North East area of Italy, which is the territory of competence of the IZSVe. In fact, these figures were identified as key stakeholders for the communication with pregnant women: in particular, the social media monitoring activities revealed that gynaecologists are the most authoritative figure for pregnant women to receive information on food risks and how to eat during pregnancy.
To learn more, the flyer referred to the website Alimenti & Gravidanza (www.alimentigravidanza.it ), more recently translated also into English (Foods & Pregnancy, www.foodspregnancy.com ). On the website, the user can consult different pages dedicated to the main pathogens and risky foods for pregnant women: it offers scientific and epidemiological information revised by microbiological experts of the IZSVe and a comprehensive list of all the good hygienic practices to reduce risks while purchasing, preparing, eating and storing foods. The Italian version of the website includes also some interactive games to help users to check their understanding of the information and good practices reported, inspired by a gamification of learning approach.
To broaden the reach of the campaign at a national level, a one-month advertising campaign through Facebook Ads was conducted. But most of all, the website was designed and developed implementing basic but effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) techniques, that still today allow the website to rank in the top positions of Google search results pages for relevant keywords about food risks and how to eat during pregnancy. In the first six month of 2022, the website averaged nearly 1,000 visits per day, without any other promotion activity.
For further information
Visit the website at this link: www.foodspregnancy.com
Read the paper Don’t Worry, Honey: It’s Cooked’: Addressing Food Risk during Pregnancy on Facebook Italian Posts
Latest Articles
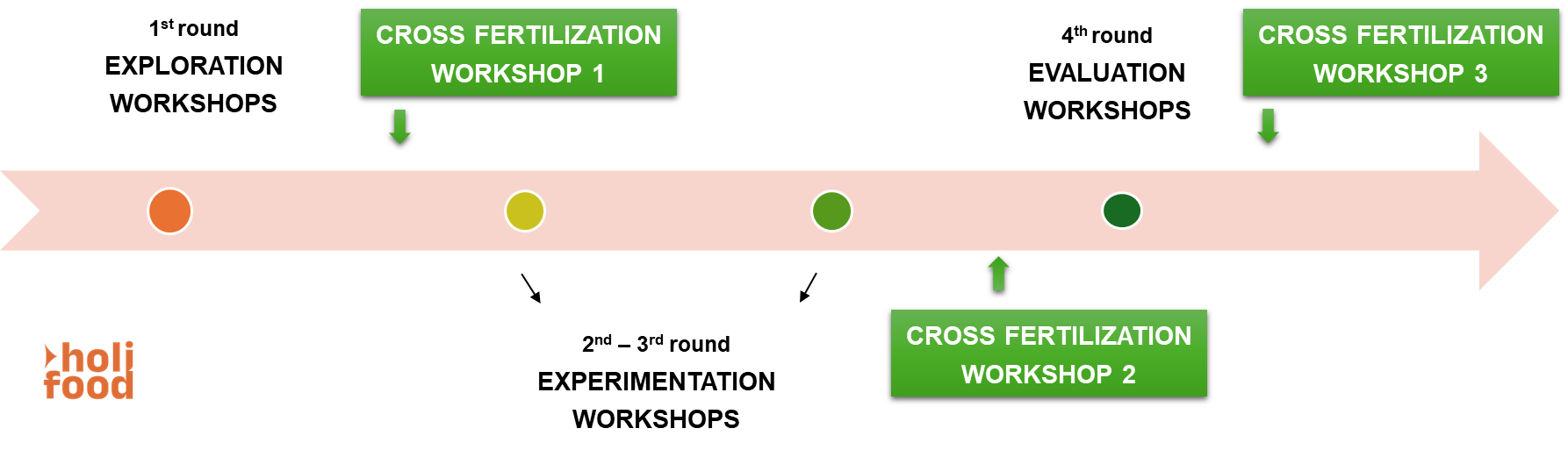
Towards holistic, AI-driven emerging risk assessment: catching stakeholders’ needs in Living Labs
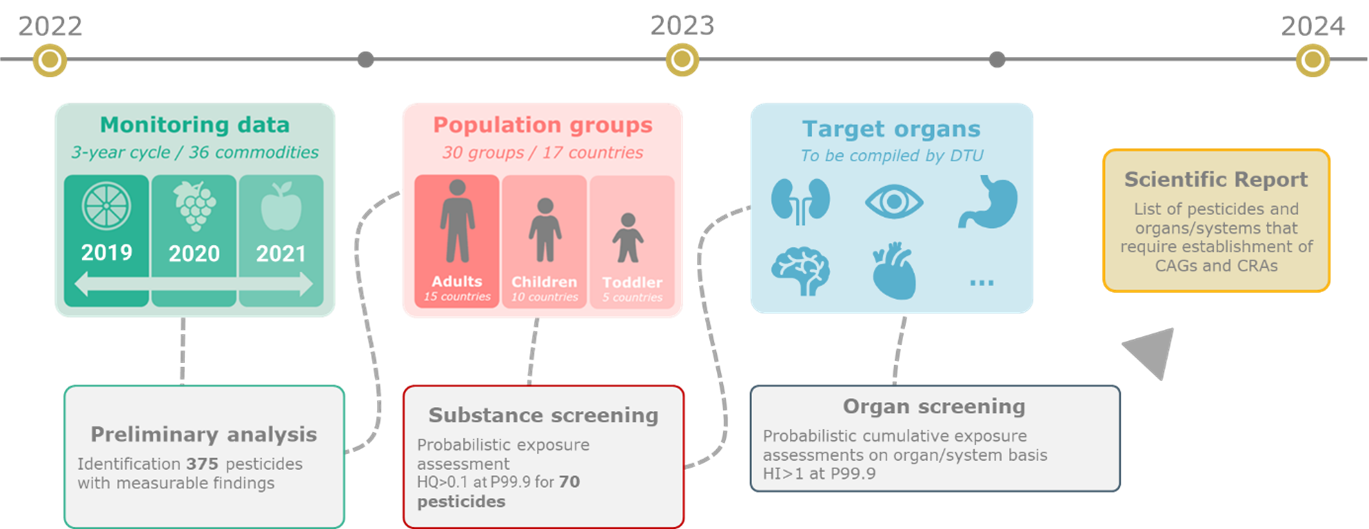
Protecting public health: understanding the importance of cumulative risk assessment of pesticides

SCAR consultation workshop on Sustainable Food Systems: highlights from EU FOOD SAFETY PLATFORM

Pioneering advances in the EU Food Safety System: highlights from the first EU Food Safety Forum
Food4Future_cz

New Tools for Preventing Harmful Bacteria in Ready-to-Eat Foods


